Table of Contents
ToggleEssential Guide to Choosing the Right Gimbal for Photography and Videography
Gimbal photography is a modern technology and a beneficial instrument for photography and videography. However, most photographers don’t use gimbals and do not know their benefits. Before this article, I had been using gimbals for the past year. It’s a terrific instrument for photography. Without using it, no one can realize its potential.
Gimbal photography uses a gimbal stabilizer to achieve smooth, shake-free footage or stills while shooting handheld. Gimbals counterbalance the camera’s weight and electronically counteract any unwanted camera movements, resulting in professional-looking, cinematic shots.
There are different types of gimbals, each serving a specific purpose.
Now, let’s move on to learning more about gimbals.
What is a Gimbal?
A gimbal is a mechanical device with motors and sensors that actively stabilize a camera when you are moving your camera up, down, left, right, and running, allowing for smooth, fluid movement even when the camera is handheld. Mainly, it is used for stabilizing your camera during any movement.
I think it’s better than a tripod in some cases. Imagine a tripod that actively counteracts your movements instead of just holding the camera still.

Gimbals use built-in motors and sensors to detect and compensate for unwanted camera shake, resulting in professional-looking, cinematic footage.
This is particularly beneficial for:
Videography
Photography
Videography:

Gimbals excel in capturing smooth, cinematic footage, ideal for weddings, events, vlogging, and action sequences. If we talk in detail about that, gimbals offer numerous benefits for videography, making them a valuable tool for creators of all levels. Here are some key advantages:
1. Smooth, Stabilized Footage:
Gimbals eliminate camera shake, resulting in professional-looking, cinematic footage. This is especially crucial when shooting handheld, as even the slightest hand movements can translate to shaky video. Smoothness is essential for creating a polished and engaging viewing experience.
2. Dynamic Camera Movements:
Gimbals allow for smooth panning, tilting, and rolling movements, enabling creative and dynamic shots. This opens up possibilities for following subjects, capturing sweeping landscapes, and achieving unique perspectives.
3. Improved Low-Light Performance:
Camera shake can be more pronounced in low-light conditions, leading to blurry footage. Gimbals compensate for this by actively stabilizing the camera, allowing for sharper and clearer images even in low-light environments.
4. Increased Versatility:
Gimbals offer greater flexibility compared to tripods. They enable you to move freely and capture footage in various situations, from weddings and events to action sequences and travel vlogs.
5. Creative Control:
Gimbals provide various modes and settings, allowing you to customize the level of stabilization and camera movement. This gives you more creative control over your shots and the overall feel of your video.
Photography:

Gimbals can also be used for still photography, especially in situations where you need to move around quickly or capture dynamic angles. Gimbals offer several benefits for handheld photography, making them a valuable tool for capturing dynamic and professional-looking images:
1. Sharper Images:
\Gimbals eliminate camera shake caused by natural hand movements, resulting in sharper and clearer photos. This is especially crucial when using long telephoto lenses or shooting in low-light conditions.
2. Dynamic Angles and Movements:
Gimbals allow for smooth panning, tilting, and rolling movements, enabling you to capture unique perspectives and dynamic compositions. This is ideal for:
- Sports Photography: Following athletes in action.
- Wildlife Photography: Tracking animals in their environment.
- Event Photography: Capturing candid moments and crowd interactions.
- Travel Photography: Creating immersive and engaging shots.
3. Creative Control:
Gimbals provide various modes and settings, allowing you to customize the level of stabilization and camera movement. This gives you more creative control over your shots and the overall feel of your image.
4. Increased Versatility:
Gimbals offer greater flexibility compared to tripods. They enable you to move freely and capture shots in various situations, even when you need to react quickly or follow unpredictable subjects.
5. Improved Low-Light Performance:
Camera shake can be more pronounced in low-light conditions, leading to blurry images. Gimbals compensate for this by actively stabilizing the camera, allowing for sharper and clearer photos even in challenging lighting situations.
Overall, gimbals significantly enhance the quality and versatility of handheld photography, making them a popular choice for photographers who want to capture dynamic and professional-looking images.
Why Gimbals are Needed: General Overview
Gimbals are not essential for all photography, but they offer significant advantages in specific situations:
- Smoothness: Gimbals eliminate camera shake, resulting in professional-looking, cinematic footage or stills.
- Dynamic Angles: Gimbals allow for smooth panning, tilting, and rolling movements, enabling creative and dynamic shots.
- Low-Light: Gimbals can help capture sharper images in low-light conditions by compensating for camera shake.

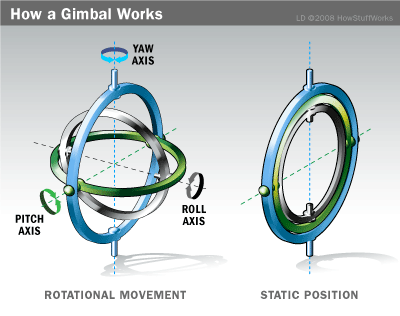
Axis of Gimbals Understanding
Before understanding the different types of gimbals, it’s crucial to grasp the concept of axis. Without a clear understanding of axis, we cannot fully comprehend how gimbals function.
A gimbal’s Axis are the imaginary lines around which it rotates to provide stability for a mounted object, typically a camera. Most commonly, gimbals have three Axis:
- Pitch Axis: This axis allows the gimbal to tilt the camera up and down.
- Roll Axis: This axis allows the gimbal to tilt the camera forward and backward (clockwise and counterclockwise).
- Yaw Axis: This axis allows the gimbal to rotate the camera left and right.

By freely rotating around these axes, the gimbal counteracts unwanted movements and vibrations, keeping the mounted object (like a camera) level and stable, resulting in smooth footage.

Types of Gimbals:

There are various types of gimbals, each with different features and capabilities:
- Single-Axis Gimbals
- Two-Axis Gimbals
- Three-Axis Gimbals
Single-Axis Gimbals:

Single-axis gimbals are the most basic type of gimbal, offering stabilization on only one axis, typically either the tilt or the roll axis.
Features:
- Lightweight and compact: They are generally smaller and lighter than other gimbal types, making them easier to carry and handle.
- Simple to use: They often have fewer buttons and settings compared to multi-axis gimbals, making them user-friendly for beginners.
- Affordable: Single-axis gimbals are typically the most affordable option among different gimbal types.
Uses:
- Basic stabilization: They can be helpful for still photography, particularly when using long telephoto lenses, to reduce camera shake and capture sharper images.
- Limited videography: They can be used for basic videography, but their limited stabilization capabilities might not be sufficient for more demanding shots.
- Smartphone stabilization: Many single-axis gimbals are specifically designed for smartphones, offering a convenient way to capture smoother and steadier mobile videos.
Common scenarios where single-axis gimbals can be useful:
- Travel photography: When using a telephoto lens to capture distant landscapes or wildlife.
- Event photography: To help stabilize shots in crowded or fast-paced environments.
- Casual vlogging: For basic vlogging where smooth footage is desired but complex camera movements are not necessary.
Overall, single-axis gimbals are a good option for those who want a simple and affordable way to improve the stability of their photos and videos, especially when working with smartphones or telephoto lenses.
Two-Axis Gimbals:

Two-axis gimbals offer a significant step up in stabilization compared to single-axis models. They provide control on two axes, typically the tilt and roll axes.
Features:
- More stabilization: Compared to single-axis gimbals, they offer smoother footage and better control over camera shake, making them more suitable for both still photography and videography.
- Compact and portable: While larger than single-axis gimbals, they are still relatively compact and easy to carry.
- User-friendly: They often have intuitive controls and settings, making them accessible to a wider range of users.
- Affordable: Two-axis gimbals offer a good balance between price and functionality, making them a popular choice for hobbyists and aspiring creators.
Uses:
- Still photography: They are ideal for capturing sharper images, especially when using longer focal lengths or telephoto lenses.
- Videography: They significantly improve the smoothness and quality of video footage, allowing for more dynamic and professional-looking results.
- Smartphone stabilization: Many two-axis gimbals are specifically designed for smartphones, offering a convenient way to capture smoother and steadier mobile videos.
Common scenarios where two-axis gimbals can be useful:
- Event photography: Capturing candid moments and crowd interactions with improved stability.
- Sports photography: Tracking athletes in action with smoother panning and tilting movements.
- Travel photography: Creating immersive and engaging shots with better control over camera shake.
- Vlogging: Improving the overall quality and professionalism of vlogging content.
Overall, two-axis gimbals offer a significant improvement in stabilization for both photography and videography, making them a versatile and valuable tool for creators of all levels.
Three-Axis Gimbals:

Three-axis gimbals are the top of the line in terms of stabilization, offering complete control over all three axes: tilt, roll, and pan. These are considered the industry standard for professional videography and photography.:
Features:
- Unmatched stabilization: They provide the smoothest and most professional-looking footage, eliminating camera shake on all axes.
- Creative control: The ability to control all three axes allows for a wider range of creative camera movements, including:
- Smooth panning and tilting
- 360-degree rotations
- Dynamic tracking shots
- Complex camera angles
- Advanced features: Many three-axis gimbals offer additional features like:
- Timelapse and motion lapse modes
- Object tracking
- Auto-calibration
- Mobile app control
Uses:
- Professional videography: Three-axis gimbals are essential for capturing high-quality, cinematic footage for:
- Feature films
- Music videos
- Commercials
- Documentaries
- Weddings and events
Advanced photography: They can be used for:
- Sports photography to track athletes in action
- Wildlife photography to capture animals in their natural environment
- Architectural photography to create stunning panoramas
- Real estate photography to showcase properties smoothly Common
scenarios where three-axis gimbals are used:
Capturing action sequences: Following fast-paced movements with perfect stability.
Creating cinematic shots: Adding professional polish and smooth transitions to video footage.
Achieving dynamic compositions: Utilizing the full range of camera movements for creative storytelling.
Overall, three-axis gimbals are the most powerful and versatile option for creators who demand the highest level of stabilization and creative control in their videography and photography.
Additional Considerations:
- Smartphone Gimbals: These are a specialized category of gimbals designed for smartphones and offer similar stabilization capabilities within their size and weight limitations.
- Payload Capacity: Different gimbals have varying payload capacities, so ensure the chosen gimbal can handle the weight of your camera and lens setup. Choosing the right gimbal depends on your specific needs and budget:
- For basic stabilization: A single-axis or two-axis gimbal might suffice.
- For professional videography and dynamic photography: A three-axis gimbal is highly recommended.

The basic difference among three types of gimbals:
The main difference between single-axis, double-axis, and three-axis gimbals lies in the number of axes they stabilize:
Single-axis:
- Stabilizes only on one axis, typically tilt or roll.
- Offers basic stabilization for still photography and limited videography.
- Lightweight, compact, and affordable.
.
Two-axis:
- Stabilizes on two axes, typically tilt and roll.
- Provides significant improvement in stabilization compared to single-axis.
- Suitable for both still photography and videography.
- Still relatively compact and user-friendly.
- Good balance between price and functionality.
Three-axis:
- Stabilizes on all three axes: tilt, roll, and pan.
- Offers the most comprehensive stabilization and creative control.
- Ideal for professional videography and advanced photography.
- Enables smooth panning, tilting, and 360-degree rotations.
- Often includes advanced features like timelapse, object tracking, and mobile app control.
- Heavier, more complex, and usually more expensive.
In essence:
- Single-axis: Basic stabilization for simple needs.
- Two-axis: Good balance between price and performance for most users.
- Three-axis: Professional-level stabilization and creative control for demanding applications.
Choosing the right gimbal depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider the level of stabilization you require, the type of content you create, and your comfort level with operating the gimbal.
Factors to Consider When Buying a Gimbal:

Here are some key factors to consider when buying a gimbal:
1. Camera Compatibility:
- Ensure the gimbal is compatible with your camera and lens setup. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for supported camera models and lens weights.
- Some gimbals are designed specifically for smartphones, while others are meant for larger cameras and lenses.
2. Payload Capacity:
Choose a gimbal that can handle the weight of your camera and lens setup comfortably. Exceeding the payload capacity can put stress on the motors and affect stabilization performance.
3. Battery Life:
Consider the gimbal’s battery life and how long it can last on a single charge. This is crucial if you plan to use the gimbal for extended periods or in situations where you may not have access to power.
4. Features:
Look for features that enhance your workflow and creative control.
Some features to consider include:
- Auto-calibration: Automatically adjusts the gimbal for optimal performance.
- Panning modes: Allows for smooth panning movements.
- Object tracking: Tracks a specific subject within the frame.
- Timelapse and motion lapse modes: Creates cinematic time-lapse sequences.
- Mobile app control: Provides control over the gimbal and camera settings through your smartphone.
5. Size and Weight:
Consider the size and weight of the gimbal, especially if you plan to travel with it frequently. A lighter gimbal will be easier to carry and use for extended periods.
6. Price:
Gimbals range in price depending on their capabilities and features. Set a budget and choose a gimbal that offers the features you need within your price range.
7. User Reviews and Brand Reputation:
- Research user reviews and compares different gimbal models to get a sense of their performance, reliability, and ease of use.
- Look for reputable brands known for their quality and customer support.

Additional Factors:
- Ergonomics: Choose a gimbal that feels comfortable to hold and operate for extended periods.
- Noise Level: Some gimbals can be noisy, which might be an issue for certain shooting situations.
- Warranty: Consider the warranty offered by the manufacturer.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the right gimbal that meets your needs and budget and helps you capture smooth, professional-looking footage.
Gimbals vs. Tripods: Gimbals and tripods serve different purposes:
- Gimbals: Ideal for smooth, handheld shots and dynamic movement.
- Tripods: Provide excellent stability for static shots and long exposures. Both can be valuable tools, but the choice depends on your specific shooting needs.
Types of Photography Gimbals are Needed For: Gimbals are particularly useful for:
- Videography: Gimbals are almost essential for capturing smooth, professional-looking video footage.
- Action Photography: Gimbals allow for stable shots while moving or tracking subjects.
- Event Photography: Gimbals can help capture dynamic angles and smooth footage of weddings, concerts, and other events.
- Travel Photography: Gimbals can be helpful for capturing handheld shots while traveling and exploring.
Photography vs. Videography:
Gimbals are primarily used for videography but can also be beneficial for specific types of photography, especially when capturing dynamic shots or working in low-light conditions.
Conclusion:
Gimbals are powerful tools for capturing smooth, professional-looking footage and stills, especially when shooting handheld. While not essential for all photography, they offer significant advantages in specific situations and can elevate your videography and dynamic photography skills.


A person essentially lend a hand to make severely articles I’d state. That is the very first time I frequented your website page and so far? I surprised with the research you made to create this actual put up incredible. Excellent activity!
Thank you so much for your kind words! I’m really glad the post made a great first impression. I truly appreciate your support, and I hope you continue to enjoy the upcoming content as well!
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find It truly useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something back and aid others like you helped me.
Heya! Welcome, and thank you so much for your kind words. I’m really glad the blog could help you out—it means a lot. Looking forward to seeing you around more, and I’m sure you’ll inspire others too. Let’s keep sharing and growing together!